Blake Lively and Ryan Reynolds’ daughters stole the show at a concert. Fans couldn’t stop talking about a detail they noticed about the girls, who rarely appear in public with their mom.
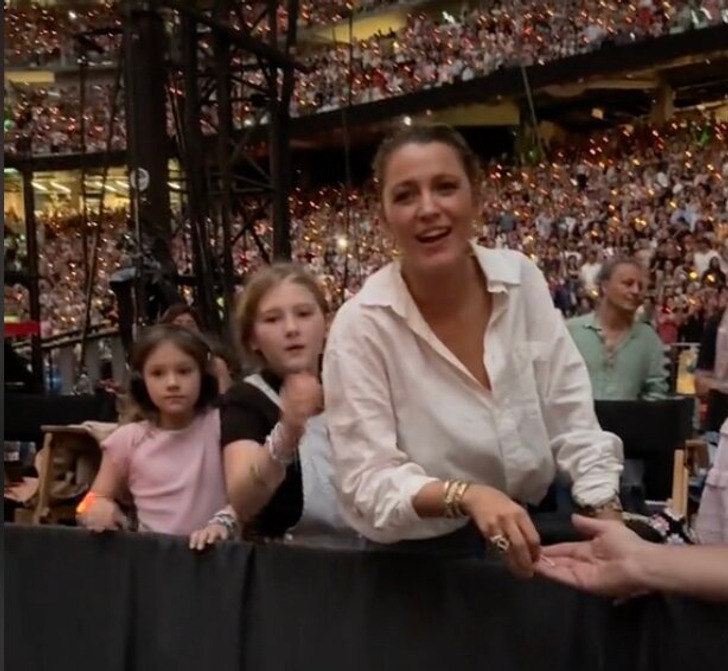

Blake Lively and Ryan Reynolds’ daughters made a rare public appearance, joining their mother at Taylor Swift’s Eras Tour show in Madrid on May 29. Videos shared on social media captured the family enjoying the concert from the VIP section, where fans couldn’t help but notice the girls’ striking resemblance to their famous mother.
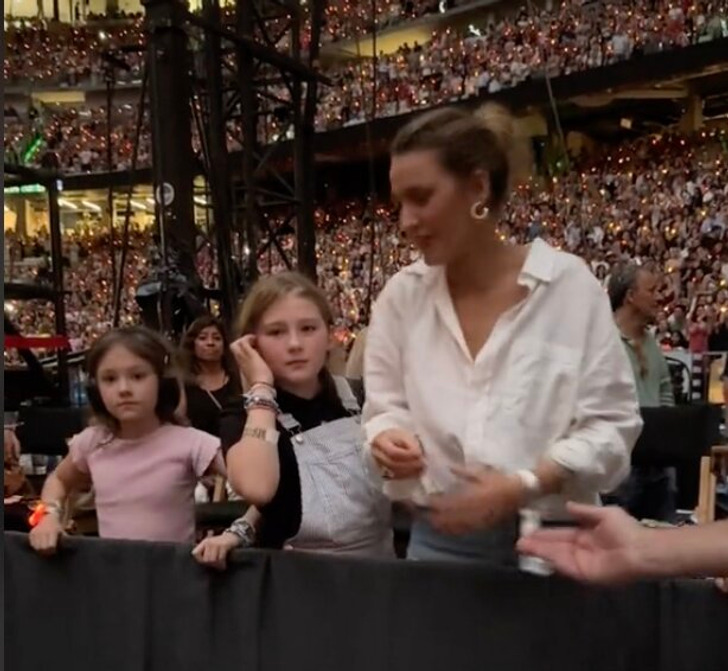
Lively went for a laid-back but trendy vibe during the outing, sporting a neat white button-up shirt paired with denim shorts and stylish gold hoop earrings. Her blonde hair was styled in a loose, pretty down-do, adorned with clips that added a touch of flair with a side part.
The mother and daughters appeared to be thoroughly enjoying the performance, engaging in socializing and exchanging bracelets. Videos capturing their outing have been widely circulated on social media platforms.
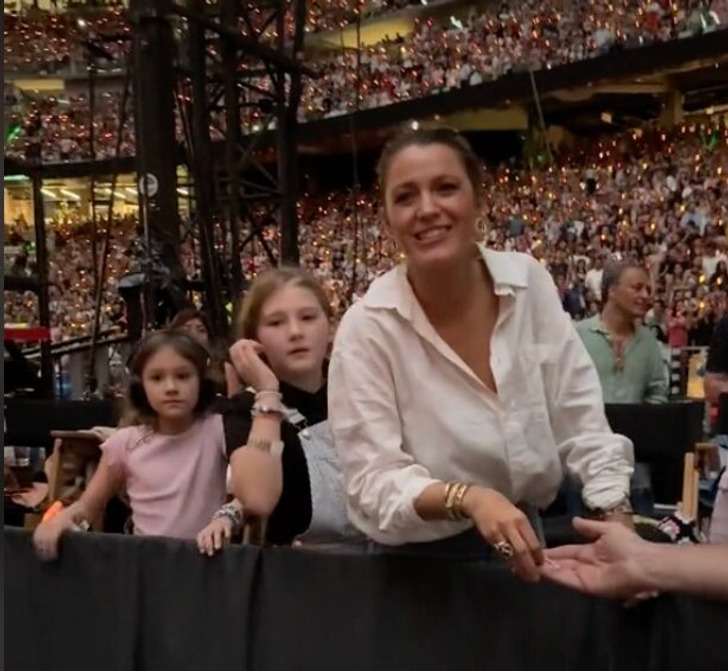

However, fans were quick to notice the strong resemblance between Lively and her daughters, flooding social media with comments. Admirers gushed over the girls, saying things like, “They have their momma’s face. So cute,” “Blake with her minis,” or “Blake’s babies look like their mama, and I’m sure they’re kind too!!” someone else wrote.
On the contrary, another fan noticed a resemblance to her husband, writing, “They look so much like Ryan.”

Now, people are buzzing with speculation about whether Swift has revealed the name of Lively and Reynolds’ fourth child in her latest album. This is because Swift often includes their kids’ names in her songs.
Reynolds humorously addressed the speculation, saying, “We always wait for Taylor to tell us what the child’s name will be.”
Blake Lively’s public outings and interactions offer a peek into their family life.
Circus lion was locked up for 20 long years, now watch his reaction when he’s released
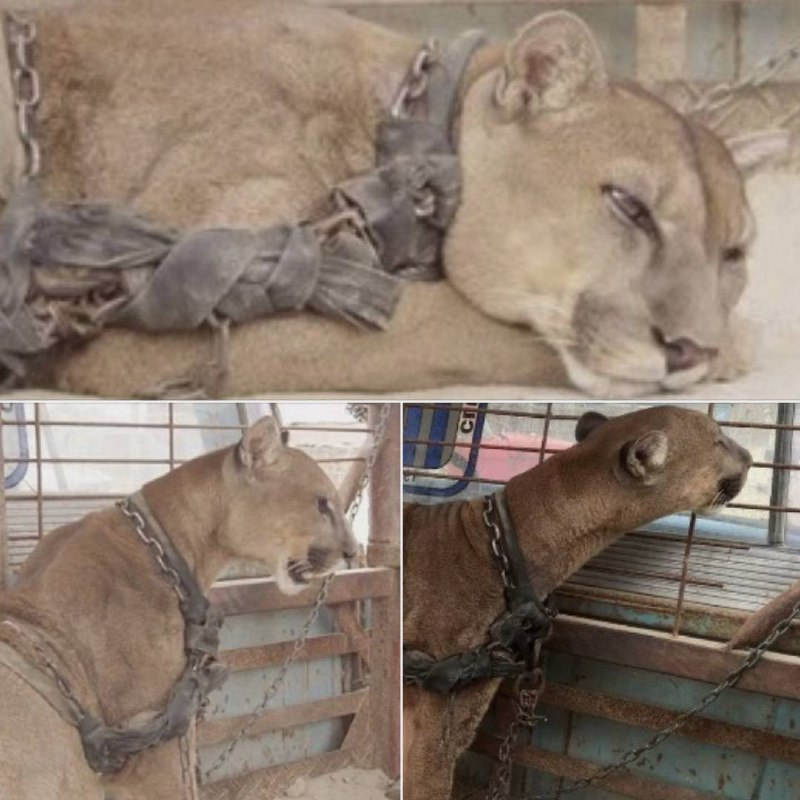

Animals hold a special place in my heart, and the idea of a mountain lion, especially a majestic one like Mufasa, being chained in a truck bed is simply heartbreaking.
Sadly, that was Mufasa’s reality. He was part of a traveling circus in Peru, forced to endure a miserable existence for people’s entertainment and his owner’s profit.
Thankfully, a beacon of hope emerged in the form of animal rights activists.
Many animals still face abuse and neglect in circuses, zoos, and shows. While recent years have seen some improvements, there’s a long road ahead. Countless creatures are confined to cramped spaces, denied the lives they deserve.
Mufasa, the magnificent mountain lion, was discovered chained to a pickup truck in Peru. For twenty long years, he was imprisoned in a life he never wanted.

Though his freedom came later in life, it arrived nonetheless. In 2015, after months of dedicated effort, Animal Defenders International, an animal rights organization, secured his release. They encountered Mufasa while shutting down a Peruvian circus.
Freedom had a profound impact on Mufasa’s well-being. He was finally free from the shackles of anxiety and oppression, experiencing the fundamental right all wild creatures deserve – to roam free in their natural habitat and live on their own terms.
Mufasa’s rescue story is heartwarming, and the video below captures his first steps towards freedom – a truly beautiful moment!
Tragically, after his rescue, Mufasa’s health, compromised by twenty years of captivity, began to decline. He succumbed to kidney failure and other age-related issues in 2015, according to Animal Defenders International.
Yet, his story serves as a powerful reminder.
Mufasa, a gentle giant who loved a good scratch, may not have had a longer time in the Amazon rainforest, but his brief taste of freedom is far preferable to a lifetime of captivity.
No animal should ever endure what Mufasa did.



Leave a Reply